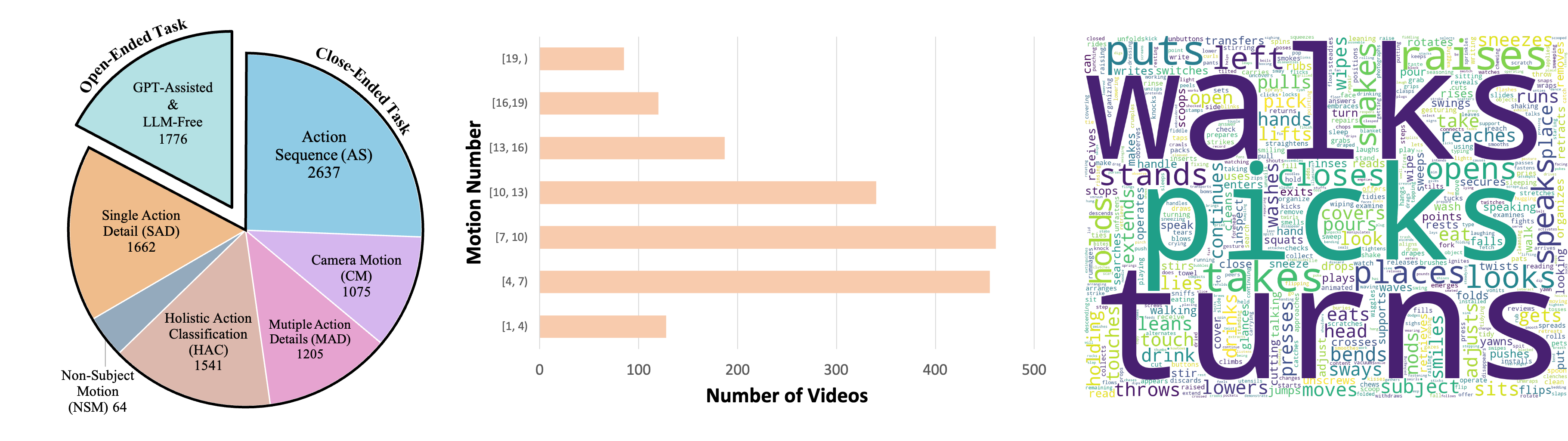
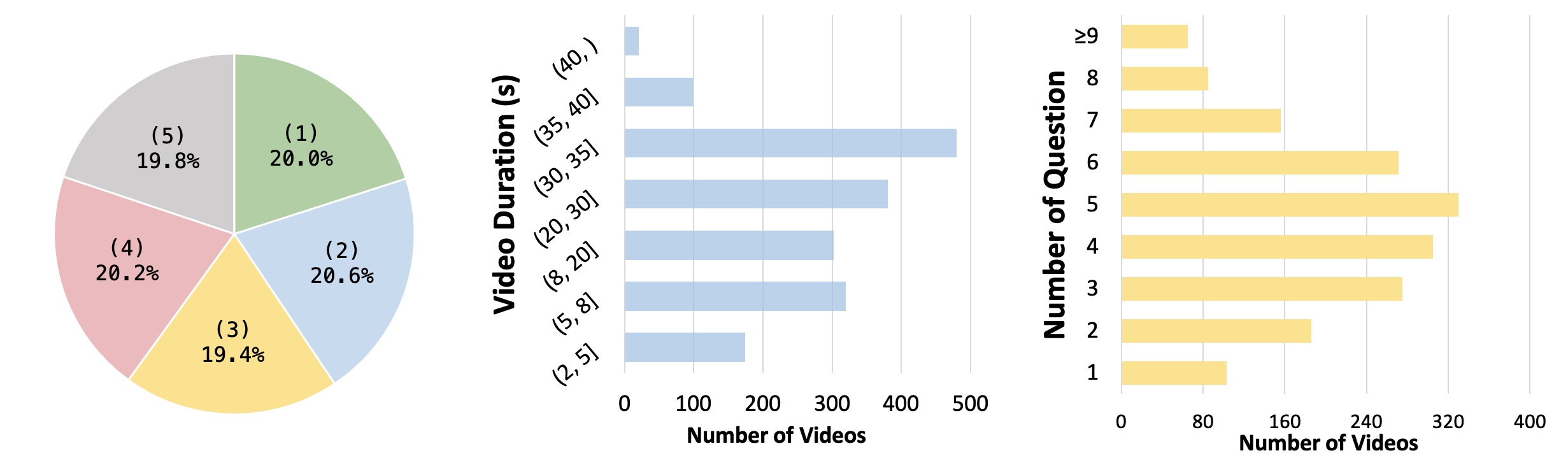
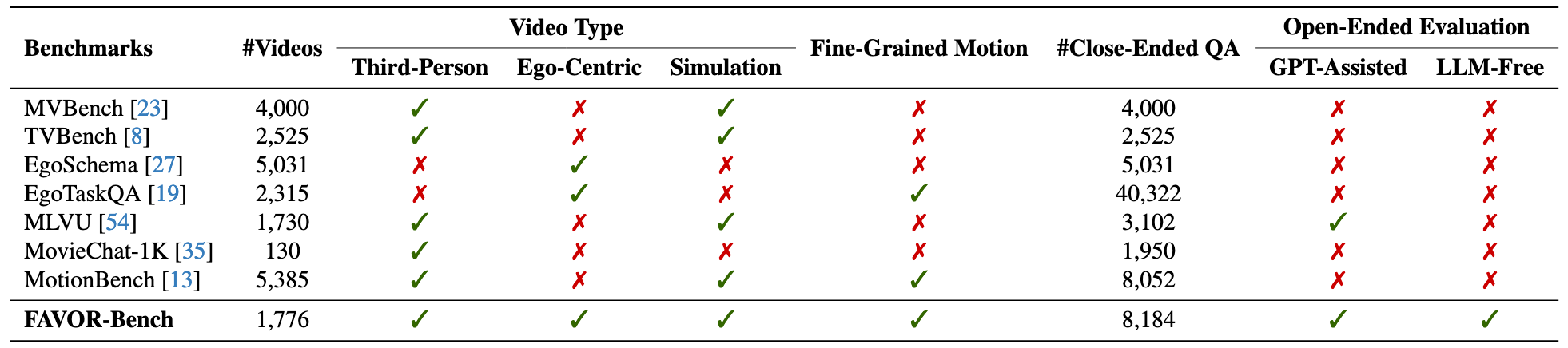
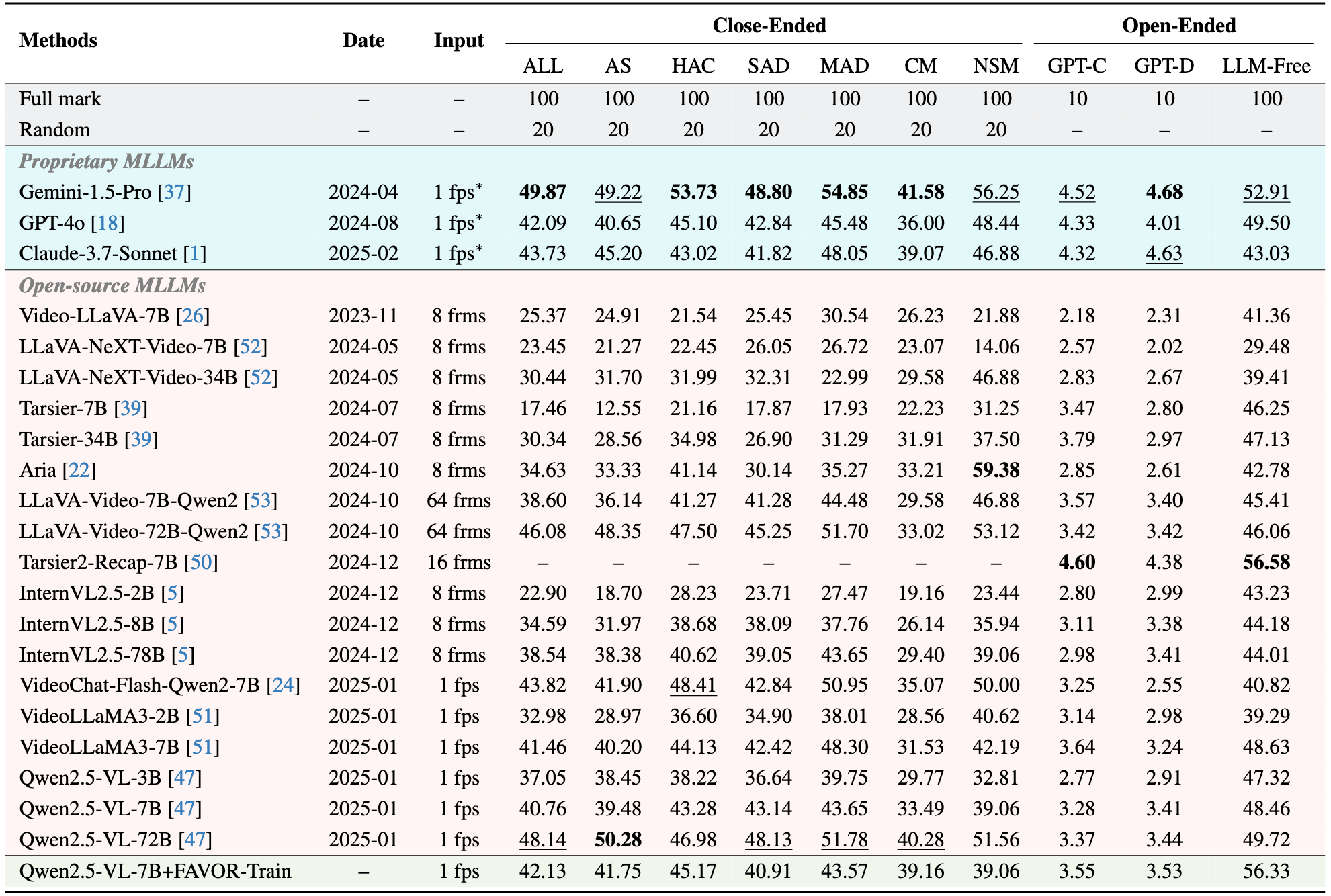
Evaluation results on FAVOR-Bench. Click on a specific indicator (such as ALL) to view the corresponding ranking list.
| # | Model | Date | Input | Close-Ended | Open-Ended | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ALL | AS | HAC | SAD | MAD | CM | NSM | GPT-C | GPT-D | LLM-Free | ||||
| Gemini-1.5-Pro | 2024-04 | 1 fps* | 49.87 | 49.22 | 53.73 | 48.80 | 54.85 | 41.58 | 56.25 | 4.52 | 4.68 | 52.91 | |
| GPT-4o | 2024-08 | 1 fps* | 42.09 | 40.65 | 45.10 | 42.84 | 45.48 | 36.00 | 48.44 | 4.33 | 4.01 | 49.50 | |
| Claude-3.7-Sonnet | 2025-02 | 1 fps* | 43.73 | 45.20 | 43.02 | 41.82 | 48.05 | 39.07 | 46.88 | 4.32 | 4.63 | 43.03 | |
| Video-LLaVA-7B | 2023-11 | 8 frms | 25.37 | 24.91 | 21.54 | 25.45 | 30.54 | 26.23 | 21.88 | 2.18 | 2.31 | 41.36 | |
| LLaVA-NeXT-Video-7B | 2024-05 | 8 frms | 23.45 | 21.27 | 22.45 | 26.05 | 26.72 | 23.07 | 14.06 | 2.57 | 2.02 | 29.48 | |
| LLaVA-NeXT-Video-34B | 2024-05 | 8 frms | 30.44 | 31.70 | 31.99 | 32.31 | 22.99 | 29.58 | 46.88 | 2.83 | 2.67 | 39.41 | |
| Tarsier-7B | 2024-07 | 8 frms | 17.46 | 12.55 | 21.16 | 17.87 | 17.93 | 22.23 | 31.25 | 3.47 | 2.80 | 46.25 | |
| Tarsier-34B | 2024-07 | 8 frms | 30.34 | 28.56 | 34.98 | 26.90 | 31.29 | 31.91 | 37.50 | 3.79 | 2.97 | 47.13 | |
| Aria | 2024-10 | 8 frms | 34.63 | 33.33 | 41.14 | 30.14 | 35.27 | 33.21 | 59.38 | 2.85 | 2.61 | 42.78 | |
| LLaVA-Video-7B-Qwen2 | 2024-10 | 64 frms | 38.60 | 36.14 | 41.27 | 41.28 | 44.48 | 29.58 | 46.88 | 3.57 | 3.40 | 45.41 | |
| LLaVA-Video-72B-Qwen2 | 2024-10 | 64 frms | 46.08 | 48.35 | 47.50 | 45.25 | 51.70 | 33.02 | 53.12 | 3.42 | 3.42 | 46.06 | |
| Tarsier2-Recap-7B | 2024-12 | 16 frms | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | 4.60 | 4.38 | 56.58 | |
| InternVL2.5-2B | 2024-12 | 8 frms | 22.90 | 18.70 | 28.23 | 23.71 | 27.47 | 19.16 | 23.44 | 2.80 | 2.99 | 43.23 | |
| InternVL2.5-8B | 2024-12 | 8 frms | 34.59 | 31.97 | 38.68 | 38.09 | 37.76 | 26.14 | 35.94 | 3.11 | 3.38 | 44.18 | |
| InternVL2.5-78B | 2024-12 | 8 frms | 38.54 | 38.38 | 40.62 | 39.05 | 43.65 | 29.40 | 39.06 | 2.98 | 3.41 | 44.01 | |
| VideoChat-Flash-Qwen2-7B | 2025-01 | 1 fps | 43.82 | 41.90 | 48.41 | 42.84 | 50.95 | 35.07 | 50.00 | 3.25 | 2.55 | 40.82 | |
| VideoLLaMA3-2B | 2025-01 | 1 fps | 32.98 | 28.97 | 36.60 | 34.90 | 38.01 | 28.56 | 40.62 | 3.14 | 2.98 | 39.29 | |
| VideoLLaMA3-7B | 2025-01 | 1 fps | 41.46 | 40.20 | 44.13 | 42.42 | 48.30 | 31.53 | 42.19 | 3.64 | 3.24 | 48.63 | |
| Qwen2.5-VL-3B | 2025-01 | 1 fps | 37.05 | 38.45 | 38.22 | 36.64 | 39.75 | 29.77 | 32.81 | 2.77 | 2.91 | 47.32 | |
| Qwen2.5-VL-7B | 2025-01 | 1 fps | 40.76 | 39.48 | 43.28 | 43.14 | 43.65 | 33.49 | 39.06 | 3.28 | 3.41 | 48.46 | |
| Qwen2.5-VL-72B | 2025-01 | 1 fps | 48.14 | 50.28 | 46.98 | 48.13 | 51.78 | 40.28 | 51.56 | 3.37 | 3.44 | 49.72 | |
| Qwen2.5-VL-7B+FAVOR-Train (Ours) | -- | 1 fps | 42.13 | 41.75 | 45.17 | 40.91 | 43.57 | 39.16 | 39.06 | 3.55 | 3.53 | 56.33 | |
* Due to the API response limitations, the video input of proprietary MLLMs is restricted to 16 frames if the video is longer than 16 seconds (demoted as "1 fps*").